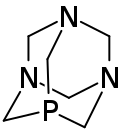
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane | |
| Other names
PTA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.239 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12N3P | |
| Molar mass | 157.157 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 260 °C (533 K)[1] |
| 23.5 g[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA) is a chemical compound with the formula C6H12N3P, a product of the substitution of a nitrogen atom of hexamethylenetetramine with a phosphorus atom. It is soluble in water, methanol, trichloromethane, acetone, ethanol and DMSO, insoluble in hydrocarbon solvent.[1] As a reagent in organic synthesis, it is used as a ligand for transition metal complexes and as a catalyst for Baylis–Hillman reactions.[1]
Preparation
Hexamethylenetetramine reacts with tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium chloride, sodium hydroxide and formaldehyde in water to obtain the product.[2]
See also
- RAPTA, a class of ruthenium complexes with the PTA ligand
References
- 1 2 3 4 Luca Gonsalvi; Maurizio Peruzzini (2010-10-15). 1,3,5-Triaza-7-phosphaadamantane (PTA). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn01186. ISBN 9780471936237.
- ↑ Donald J. Daigle; Tara J. Decuir; Jeffrey B. Robertson; Donald J. Darensbourg (2007-01-05). 1,3,5-Triaz-7-Phosphatricyclo[3.3.1.1 3,7 ]Decane and Derivatives. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 40–45. doi:10.1002/9780470132630.ch6. ISBN 9780470132630.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.