 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,3-Dihydro-1H-inden-1-one | |
| Other names
α-Hydroindone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 507957 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.337 |
| EC Number |
|
| 142414 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O | |
| Molar mass | 132.162 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless solid |
| Melting point | 38–42 °C (100–108 °F; 311–315 K) |
| Boiling point | 243–245 °C (469–473 °F; 516–518 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
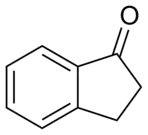
1-Indanone is the organic compound with the formula C6H4(CH2)2CO. It is one of two isomeric benzocyclopentanones, the other being 2-indanone. It is a colorless solid. 1-Indanone is a substrate for the enzyme indanol dehydrogenase.
Preparation
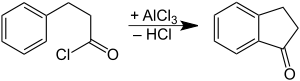
It is prepared by oxidation of indane or indene.[1] It can also be prepared by cyclization of phenylpropionic acid.
List of Drugs
- 2-Aminoindan synthesis (MDAI methodology using beta-keto-oxime formation with isoamylnitrite followed by reduction).
- Drinidene
- LNK-121[2]
- Pirandamine
- Pyrophendane
- SKF Derivatives:[3][4]
- Indane analog of nisoxetine or Prozac.[5]
References
- ↑ R. A. Pacaud, C. F. H. Allen (1938). "α-Hydroindone". Org. Synth. 18: 47. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.018.0047.
- ↑ Peter T. Lansbury, Jr. Craig J. Justman, US20100292292 (2010 to Link Medicine Corp).
- ↑ Ganellin, C. R.; Loynes, J. M.; Ridley, H. F.; Spickett, R. G. W. (1967). "Compounds Affecting the Central Nervous System. IV. Substituted 2-Benzyl-3-dialkylaminoalkylindenes and Related Compounds". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 10 (5): 826–833. doi:10.1021/jm00317a016.
- ↑ Jack David, Spickett Robert Geoffr William & Ganellin Charon Robin, U.S. Patent 3,159,634 (1964 to Smith Kline and French Laboratories Ltd).
- ↑ Jules Freedman, U.S. Patent 5,149,714 (1992 to Aventis Inc).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.