 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
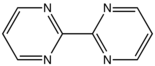
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′-Bipyrimidine | |
| Other names
2,2′-Dipyrimidine, bipyrimidyl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.383 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6N4 | |
| Molar mass | 158.164 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 113–115 °C (235–239 °F; 386–388 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2,2′-Bipyrimidine is an organic compound with the formula (C4H3N2)2. It is a derivative of the heterocycle pyrimidine. It is a white solid. The compound is used as a bridging ligand in coordination chemistry.[1]
2,2′-Bipyrimidines can be prepared by Ullmann coupling of 2-iodopyrimidines.[2]
References
- ↑ Periana, Roy A.; Taube, Douglas J.; Gamble, Scott; Taube, Henry; Satoh, Takashi; Fujii, Hiroshi (1998). "Platinum Catalysts for the High-Yield Oxidation of Methane to a Methanol Derivative". Science. 280 (5363): 560–564. Bibcode:1998Sci...280..560P. doi:10.1126/science.280.5363.560. PMID 9554841.
- ↑ Vlád, Gábor; Horváth, István T. (2002). "Improved synthesis of 2,2′-bipyrimidine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 67 (18): 6550–6552. doi:10.1021/jo0255781. PMID 12201781. S2CID 13374569.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.