| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Oxohexanedioic acid[2] | |||
| Other names
α-Ketoadipic acid 2-Ketoadipic acid α-Oxoadipic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.320 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | Alpha-ketoadipic+acid | ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
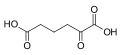
| C6H8O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 160.125 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.4 g cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | 125 °C (257 °F; 398 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
2-Oxoadipic acid, also known as α-ketoadipic acid, is an intermediate in the metabolism of lysine. The conjugate base and carboxylate is 2-oxoadipate or α-ketoadipate, which is the biochemically relevant form.
See also
References
- ↑ 2-oxoadipate - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- ↑ "Alpha-ketoadipic acid". The PubChem Project. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.