 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
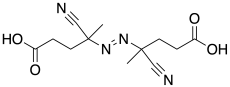
| Preferred IUPAC name
4,4′-[(E)-Diazenediyl]bis(4-cyanopentanoic acid) | |
| Other names
4,4-Azobis(4-cyanovaleric acid); 4,4-Azobis(cyanovaleric acid); 4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid); ABCVA; ACVA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.305 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 280.284 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 118 to 125 °C (244 to 257 °F; 391 to 398 K) |
| Soluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
4,4′-Azobis(4-cyanopentanoic acid) (ACPA) is a free radical initiator used in polymer synthesis.[1] ACPA is a water-soluble initiator used in both heterogeneous and homogeneous free-radical polymerizations. It is used as an initiator in reversible addition−fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT). When heated to decomposition, c. 70 °C, it releases N2 and produces 2 equivalents of reactive radicals capable of initiating polymerization.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.