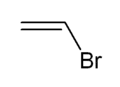 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bromoethene | |
| Other names
Vinyl bromide 1-Bromoethene Bromoethylene 1-Bromoethylene Monobromoethene Monobromoethylene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.911 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1085 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3Br | |
| Molar mass | 106.95 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless gas or liquid |
| Odor | pleasant[1] |
| Density | 1.525 g/cm3 at boiling point (liquid)
1.4933 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −137.8 °C (−216.0 °F; 135.3 K) |
| Boiling point | 15.8 °C (60.4 °F; 288.9 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| log P | 1.57 |
| Vapor pressure | 206.8 kPa at 37.8 °C |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H220, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P281, P308+P313, P377, P381, P403, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 5 °C (41 °F; 278 K) |
| 530 °C (986 °F; 803 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 9%-15%[1] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
Ca[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Vinyl bromide (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Vinyl bromide is the organobromine compound with the formula CH2=CHBr. Classified as a vinyl halide, it is a colorless gas at room temperature. It is used as a reagent and a comonomer.
Synthesis, reactions, and applications
It is produced from ethylene dibromide:
- CH2Br−CH2Br → CH2=CHBr + HBr
CH2=CHBr is mainly consumted as a comonomer to confer fire retardant properties to acrylate polymers.[2]
Vinyl bromide reacts with magnesium to give the corresponding Grignard reagent CH2=CHMgBr.[3][4]
Safety precautions
Vinyl bromide is listed in List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens as a suspected human carcinogen.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0657". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Dagani, M. J.; Barda, H. J.; Benya, T. J.; Sanders, D. C. "Bromine Compounds". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a04_405. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Dietmar Seyferth (1959). "Di-n-butyldivinyltin". Org. Synth. 39: 10. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.039.0010.
- ↑ William J. Scott, G. T. Crisp, J. K. Stille (1990). "Palladium-catalyzed Coupling of Vinyl Triflates with Organostannanes: 4-tert-butyl-1-vinylcyclohexene and 1-(4-tert-butylcyclohexen-1-yl)-2-propen-1-one". Organic Syntheses. 68: 116. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.068.0116.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0597
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0657". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- MSDS at Oxford University
- MSDS at mathesontrigas.com
- Vinyl bromide at IRIS
- Vinyl bromide at osha.gov
- IARC Summary & Evaluation of vinyl bromide
- Report on Carcinogens Background Document for Vinyl Bromide
- Synthesis of vinyl bromides
- The Kinetics of Pyrolysis of Vinyl Bromide
- UV absorption spectra
- UV Spectrum and Cross Sections
- 1H NMR spectrum
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
