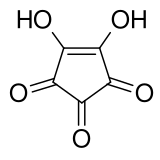
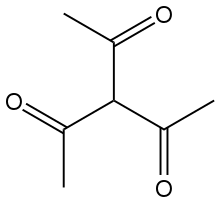
In organic chemistry, a triketone or trione is an organic compound containing three ketone (>C=O) groups. The simplest triketones, such as cyclopropanetrione and 2,3,4-pentanetrione, are only of occasional theoretical interest. More pertinent are triacetylmethane and 2,4,6-heptanetrione. Both species exist predominantly in the enol (C=CH) forms.
Occurrence and significance
Tri- and polyketones are of practical importance as intermediates in the biosynthesis of polyketides.[1] These natural products are a major source of antibiotics.
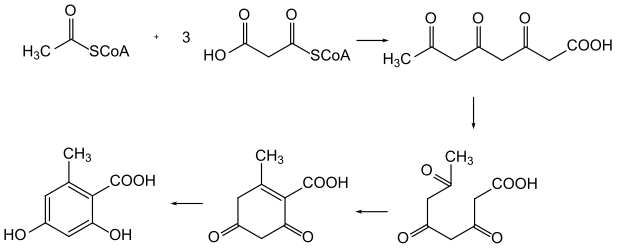
Biosynthesis of orsellinic acid from polyketide intermediate.
See also
References
- ↑ Fischbach, Michael A.; Walsh, Christopher T. (2006). "Assembly-Line Enzymology for Polyketide and Nonribosomal Peptide Antibiotics: Logic, Machinery, and Mechanisms". Chemical Reviews. 106 (8): 3468–3496. doi:10.1021/cr0503097. PMID 16895337.
External links
 Media related to Triketones at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Triketones at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.