| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,2-Trichloroethane | |||
| Other names
1,1,2-TCA vinyl trichloride beta-trichloroethane, symmetrical Trichloroethane, monochlorethylen chloride (archaic) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.061 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H3Cl3 | |||
| Molar mass | 133.40 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid[1] | ||
| Odor | sweet, chloroform-like[1] (in high concentrations) | ||
| Density | 1.435 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −37 °C (−35 °F; 236 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 110 to 115 °C (230 to 239 °F; 383 to 388 K) | ||
| 0.4% (20°C)[1] | |||
| Vapor pressure | 19 mmHg (20°C)[1] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Explosive limits | 6–15.5%[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose) |
1200 mg/kg (rat, orally)[2] | ||
LCLo (lowest published) |
13,100 mg/m3 (cat, 4.5 hr) 2000 ppm (rat, 4 hr)[3] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 10 ppm (45 mg/m3) [skin][1] | ||
REL (Recommended) |
Ca TWA 10 ppm (45 mg/m3) [skin][1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [100 ppm][1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
1,1,1-Trichloroethane; Trichloroethylene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
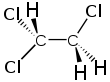
1,1,2-Trichloroethane, or 1,1,2-TCA, is an organochloride solvent with the molecular formula C2H3Cl3 and the structural formula CH2Cl—CHCl2. It is a colourless, sweet-smelling liquid that does not dissolve in water, but is soluble in most organic solvents. It is an isomer of 1,1,1-trichloroethane, and a byproduct of its manufacture.
It is used as a solvent and as an intermediate in the synthesis of 1,1-dichloroethene.[4]
1,1,2-TCA is a central nervous system depressant and inhalation of vapors may cause dizziness, drowsiness, headache, nausea, shortness of breath, and unconsciousness.[5]
Toxicology
Trichloroethane may be harmful by inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. It is a respiratory and eye irritant.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health have set occupational exposure limits to 1,1,2-Trichloroethane at 10 ppm over an eight-hour time-weighted average.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0628". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ 1,1,2-Trichloroethane toxicity
- ↑ "1,1,2-Trichloroethane". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Toxicological profile for 1,1,2-trichloroethane (PDF) (Report). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). March 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-03-05. Retrieved 2023-08-23.
- ↑ "Safety (MSDS) data for 1,1,2-trichloroethane" (PDF).
- ↑ CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards