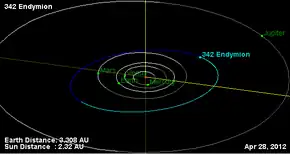
 Orbital diagram | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Max Wolf |
| Discovery date | 17 October 1892 |
| Designations | |
| (342) Endymion | |
| Pronunciation | /ɛnˈdɪmiən/[1] |
Named after | Endymion |
| 1892 K | |
| Main belt König · Bower | |
| Orbital characteristics[2] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 115.38 yr (42141 d) |
| Aphelion | 2.89687 AU (433.366 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 2.24079 AU (335.217 Gm) |
| 2.56883 AU (384.291 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.12770 |
| 4.12 yr (1503.8 d) | |
| 335.858° | |
| 0° 14m 21.793s / day | |
| Inclination | 7.34850° |
| 232.690° | |
| 224.708° | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 60.63±2.8 km |
| 6.319 h (0.2633 d) | |
| 0.0393±0.004 | |
| 10.22 | |
Endymion (minor planet designation: 342 Endymion) is a large Main belt asteroid.[2] It was discovered by Max Wolf on 17 October 1892 in Heidelberg. It was the first asteroid to receive the name of a male god.[3]
References
- ↑ "Endymion". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary.
- 1 2 "342 Endymion (1892 K)". JPL Small-Body Database. NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- ↑ Lutz D. Schmadel, Dictionary of minor planet names (6th Edition), p. 42. Springer Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg 2012, ISBN 3-642-29717-X
External links
- 342 Endymion at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 342 Endymion at the JPL Small-Body Database
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.