 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.217 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| Properties | |
| BeTe | |
| Molar mass | 136.612 g/mol |
| Density | 5.1 g/cm3 |
| Structure | |
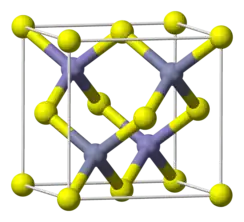
| sphalerite, cF8, Space group = F-43m, No. 216 | |
| Hazards | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 0.002 mg/m3 C 0.005 mg/m3 (30 minutes), with a maximum peak of 0.025 mg/m3 (as Be)[1] |
REL (Recommended) |
Ca C 0.0005 mg/m3 (as Be)[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
Ca [4 mg/m3 (as Be)][1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Beryllium telluride (BeTe) is a chemical compound of beryllium and tellurium. It is a crystalline solid with the lattice constant of 0.5615 nm. It is a semiconductor with a large energy gap of around 3 eV. Toxicity is unknown. Toxic hydrogen telluride gas is evolved on exposure to water.
References
- 1 2 3 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0054". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.