 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LY 300502 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
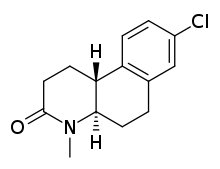
| Formula | C14H16ClNO |
| Molar mass | 249.74 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bexlosteride is a potent and noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme 5α-reductase related to finasteride and dutasteride.[1][2] It is selective for the type I isoform of the enzyme.[1] It advanced to Phase III clinical trials, but development was halted at that stage, and it was never marketed.[3][4]
See also
References
- 1 2 Chang C (2002). Androgens and androgen receptor : mechanisms, functions, and clinical application. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers. ISBN 1-4020-7188-4.
- ↑ Lednicer D (2008). Strategies for Organic Drug Synthesis and Design. New York: Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 978-0-470-19039-5.
- ↑ "Drug Profile: Bexlosteride". Adis Insight.
- ↑ Reaxys entry for bexlosteride: Reaxys Registry Number: 6635310
Drugs used in benign prostatic hyperplasia (G04C) | |
|---|---|
| 5α-Reductase inhibitors | |
| Alpha-1 blockers | |
| Steroidal antiandrogens | |
| Herbal products | |
| Others | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.