 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
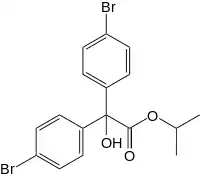
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propan-2-yl bis(4-bromophenyl)hydroxyacetate | |
| Other names
Acarol; Isopropyl 4,4'-dibromobenzilate; Phenisobromolate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.231 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H16Br2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 428.120 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid[1] |
| Density | 1.59 g/cm3 (20 °C)[1] |
| Melting point | 77 °C (171 °F; 350 K)[1] |
| 0.1 mg/L (20 °C)[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Bromopropylate is a chemical compound used as an acaricide against spider mites in apiaries and on fruit crops such as citrus and grapes.[1] It was banned by the European Union in 2011.
Preparation
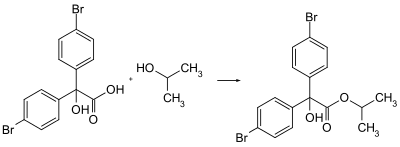
Bromopropylate is prepared by the esterification of the 4,4'-dibromo derivative of benzilic acid with isopropanol.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health

Vial of Bromopropylate
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.