 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Rhinetten, Rhinoptil |
| Other names | Methylcoffanolamine; 8-[(2-Hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amino]caffeine |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.045.795 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
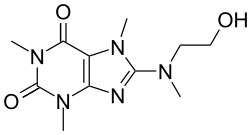
| Formula | C11H17N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 267.289 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Cafaminol (brand names Rhinetten, Rhinoptil), also known as methylcoffanolamine, is a vasoconstrictor and anticatarrhal of the methylxanthine family related to caffeine which is used as a nasal decongestant in Germany.[1][2][3][4][5][6] It was introduced in 1974 and was still in use as of 2000.[3][2]
References
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 205–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- 1 2 Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. 2000. pp. 157–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- 1 2 William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Elsevier. pp. 784–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
- ↑ Szirmai E (1969). "[A new treatment for colds using a new caffeine derivative, methylcoffanolamine]". Praxis (in German). 58 (13): 412–4. PMID 5818666.
- ↑ Walther H, Köhler E (1979). "[Human pharmacologic studies on the biologic availability and resorption of cafaminol (AWD) (proceedings)]". Pharmazie (in German). 34 (5–6): 375–6. PMID 515164.
- ↑ Rogowski M, Chodynicki S (1985). "[Use of the preparation Cafaminol in the treatment of acute rhinitis]". Wiad. Lek. (in Polish). 38 (20): 1437–40. PMID 3913153.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.