 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-(Prop-2-en-1-yl)phenol | |
| Other names
4-Allylphenol; p-Allylphenol; para-Allylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.209 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O | |
| Molar mass | 134.18 g/mol |
| Density | 1.020 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 16 °C (61 °F; 289 K) |
| Boiling point | 238 °C (460 °F; 511 K) (123 °C at 16 mmHg) |
| 2.46 g/L | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chavicol (p-allylphenol) is a natural phenylpropene, a type of organic compound.[1] Its chemical structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with a hydroxy group and a propenyl group. It is a colorless liquid found together with terpenes in betel oil.
Properties and reactions
Chavicol is miscible with alcohol, ether, and chloroform. Dimerization of chavicol gives the neo-lignan magnolol.
Uses
Chavicol is used as an odorant in perfumery and as a flavor. It is found in many essential oils, including anise and gardenia.[2]
Biosynthesis
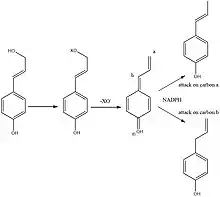
Chavicol is formed in sweet basil (Ocimum Basilicum) by the phenylpropanoid pathway via p-coumaryl alcohol. The allylic alcohol in p-coumaryl alcohol is converted into a leaving group. This then leaves thus forming a cation, this cation can be regarded as a quinone methide which then is reduced by NADPH to form either anol or chavicol.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ "Chavicol, 501-92-8".
- ↑ Daniel G. Vassao, David R. Gang, Takao Koeduka, Brenda Jackson, Eran Pichersky, Laurence B. Davina and Norman G. Lewis, Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 2006, 4, 2733-2744. DOI: 10.1039/b605407b