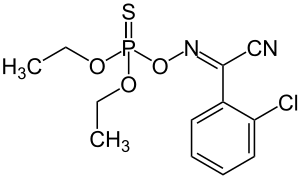
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.338 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H14ClN2O3PS | |
| Molar mass | 332.74 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chlorphoxime is an insecticide used as crop protection active ingredient.[1] Chlorphoxime is also a cholinesterase inhibitor and a neurotoxin.[2]
Properties
A study was conducted to investigate the effect of chlorophoxime for the control of fleas in kangaroo rats and hispid cotton rats. Chlorphoxime was found to be effective.[3]
In another study, the efficacy of some insecticides was investigated on certain storage pests. While phoxim, bioresmethrin and fenitrothion showed strong activity against the red-brown rice mealybug, the insecticidal activity of chlorphoxim and permethrin was low.[4]
Production
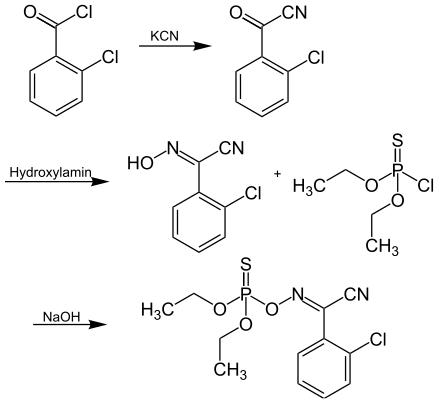
The synthesis of chlorophoxime is described in the following reaction sequence:[1]
Trade names
A crop protection product containing the active ingredient chlorophoxime is marketed under the trade name Baythion.[1]
Approval
No plant protection products containing chlorophoxime are approved in the European Union or Switzerland.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 Thomas A. Unger (1996), "Chlorphoxim", Pesticide Synthesis Handbook (in German), Elsevier, p. 312, doi:10.1016/b978-081551401-5.50240-9, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5
- ↑ University of Hertfordshire. "Chlorphoxim (Ref: OMS 1197)". Retrieved 2022-06-22.
- ↑ Bryan E. Miller, William. C. Bennett, Garth N. Graves, John R. Wheeler (1977-11-25), "Field Studies of Systemic Insecticides. II. Evaluation of chlorphoxim for control of fleas on five rodent species12", Journal of Medical Entomology (in German), vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 161–166, doi:10.1093/jmedent/14.2.161, ISSN 1938-2928, PMID 606815
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ M. A. Khan (1983-02-01), "Wirksamkeit von Insektiziden und Repellents gegen Vorratsschädlinge", Anzeiger für Schädlingskunde, Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz (in German), vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 25–29, doi:10.1007/BF01905984, ISSN 1612-4766, S2CID 31751339
- ↑ European Commission Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety: EU Pesticides Database; entry in the national plant protection product inventories of Switzerland, Austria and Germany, accessed July 20, 2022.