 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cholane[1] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1R,3aS,3bR,5aΞ,9aS,9bS,11aR)-9a,11a-Dimethyl-1-[(2R)-pentan-2-yl]hexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H42 | |
| Molar mass | 330.59 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
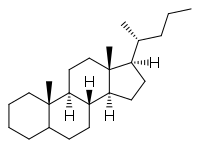
Cholane is a triterpene which can exist as either of two stereoisomers, 5α-cholane and 5β-cholane. Its name is derived from Greek: χολή (chole) meaning 'bile' in reference to its original discovery from the bile of the American bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana).[2] The compound itself has no known uses. However, various functionalized analogues are produced by plants and animals, typically in the form of sterols, steroids and bile acids (e.g. cholic acid).
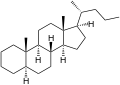 5α-Cholane
5α-Cholane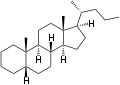 5β-Cholane
5β-Cholane
See also
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 1528. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Kurauti, Yukiti; Kazuno, Taro (January 1939). "Tetraoxycholan, Trioxycholen und Trioxy-bis-norsterocholansäure aus der Galle von Rana Catesbina Shaw". Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift für physiologische Chemie (in German). 262 (1–2): 53–60. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1939.262.1-2.53.
External links
- Cholanes at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.