 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
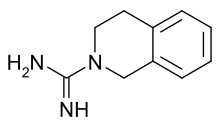
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-carboximidamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.155 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Debrisoquine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N3 | |
| Molar mass | 175.23032 |
| Pharmacology | |
| C02CC04 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Debrisoquine is a derivative of guanidine. It is an antihypertensive drug similar to guanethidine. Debrisoquine is frequently used for phenotyping the CYP2D6 enzyme, a drug-metabolizing enzyme.[2]
See also
The guanidine part of the molecule also appears in guanoxan and guanadrel.
- The 7-bromo analog of Debrisoquine is called Guanisoquin.
References
- ↑ Debrisoquine – Compound Summary, PubChem.
- ↑ Fuhr, U.; Jetter, A.; Kirchheiner, J. (2007). "Appropriate Phenotyping Procedures for Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters in Humans and Their Simultaneous Use in the "Cocktail" Approach". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 81 (2): 270–283. doi:10.1038/sj.clpt.6100050.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.