| Gangliocytic paraganglioma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Micrograph of a gangliocytic paraganglioma. H&E stain. | |
| Pronunciation |
|
| Specialty | Pathology |
A gangliocytic paraganglioma is a rare tumour that is typically found in the duodenum and consists of three components: (1) ganglion cells, (2) epithelioid cells (paraganglioma-like) and, (3) spindle cells (schwannoma-like).[1]
Symptoms and signs
The most common presentation is gastrointestinal bleed (~45% of cases), followed by abdominal pain (~43% of cases) and anemia (~15% of cases).[2]
Pathology
GP consist of three components (1) ganglion cells, (2) epithelioid cells (neuroendocrine-like), and (3) spindle cells (schwannoma-like). The microscopic differential diagnosis includes poorly differentiated carcinoma, neuroendocrine tumour and paraganglioma.[1]
GPs may be sporadic or arise in the context neurofibromatosis type 1.
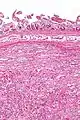 Intermed. mag.
Intermed. mag. Intermed. mag.
Intermed. mag.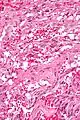 Very high mag.
Very high mag.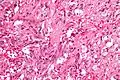 Very high mag.
Very high mag.
See also
References
- 1 2 Wong, A.; Miller, AR.; Metter, J.; Thomas, CR. (Mar 2005). "Locally advanced duodenal gangliocytic paraganglioma treated with adjuvant radiation therapy: case report and review of the literature". World J Surg Oncol. 3 (1): 15. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-3-15. PMC 554089. PMID 15740625.
- ↑ Okubo, Y.; Wakayama, M.; Nemoto, T.; Kitahara, K.; Nakayama, H.; Shibuya, K.; Yokose, T.; Yamada, M.; Shimodaira, K.; Sasai, Daisuke; Ishiwatari, Takao; Tsuchiya, Masaru; Hiruta, Nobuyuki (2011). "Literature survey on epidemiology and pathology of gangliocytic paraganglioma". BMC Cancer. 11: 187. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-187. PMC 3141762. PMID 21599949.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.