 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Iodocyclohexane | |
| Other names
Cyclohexyl iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.962 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11I | |
| Molar mass | 210.058 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless to slightly reddish yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.624 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 71 °C (160 °F; 344 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Chlorocyclohexane Bromocyclohexane Fluorocyclohexane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
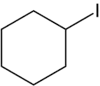
Iodocyclohexane is an organoiodine compound with the chemical formula C6H11I.[1][2]
Synthesis
Iodocyclohexane has been prepared by the addition of hydrogen iodide to cyclohexene.[3]
Alternatively, it can be prepared by the reaction of cyclohexane and iodoform.[4]
Physical properties
Iodocyclohexane forms colorless to slightly reddish yellow liquid. It is soluble in ethanol, ether, and acetone.[1]
Uses
The compound has been used as reagent in demethylation of aryl methyl ethers in DMF under reflux condition.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "B24840 Iodocyclohexane, 98%, stab. with copper". Alfa Aesar. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ "Iodocyclohexane". Sigma Aldrich. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
- ↑ Stone, Herman; Shechter, Harold (1951). "Iodocyclohexane". Organic Syntheses. 31: 66. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.031.0066.
- ↑ "Synthesis of iodocyclohexane from cyclohexane and iodoform" (PDF). oc-praktikum.de. Retrieved 21 June 2023.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.