| Lepidosperma asperatum | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Clade: | Commelinids |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Lepidosperma |
| Species: | L. asperatum |
| Binomial name | |
| Lepidosperma asperatum | |
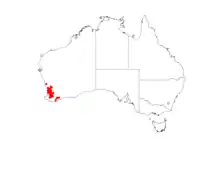 | |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[3][4] | |
|
Lepidosperma leptostachyum var. asperatum Kük. | |
Lepidosperma asperatum is a sedge (in the family Cyperaceae) that is endemic to Western Australia.[1] It was first described in 1941 by Georg Kükenthal as Lepidosperma leptostachyum var. asperatum,[5] but was elevated to species status in 2012 by Karen Wilson and Russell Barrett.[3][2]
Distribution
It is found in the IBRA regions of the Avon Wheatbelt, the Geraldton Sandplains, the Jarrah Forest, the Mallee biogeographic region, and the Swan Coastal Plain.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 "Lepidosperma asperatum". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions.
- 1 2 Barrett, R.L. & Wilson, K.L. (2012). "A review of the genus Lepidosperma Labill. (Cyperaceae: Schoeneae)". Australian Systematic Botany. 25 (4): 234–235, Fig. 5. doi:10.1071/SB11037. S2CID 83770459.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 "Lepidosperma asperatum". Australian Plant Name Index, IBIS database. Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Australian Government.
- ↑ "Lepidosperma asperatum (Kük.) R.L.Barrett | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science". Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ↑ Kükenthal, G. (1941). "Vorarbeiten zu einer Monographie der Rhynchosporoideae. XI". Repertorium Novarum Specierum Regni Vegetabilis. 50 (6–12): 117. doi:10.1002/fedr.19410500606. ISSN 0375-121X.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.