| Mark 32 torpedo | |
|---|---|
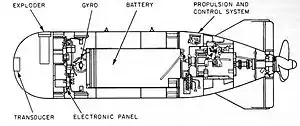 Diagram of the Mark 32 torpedo | |
| Type | Acoustic torpedo[1] |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1950-1955[1] |
| Used by | United States Navy |
| Production history | |
| Designer | General Electric[1] Ordnance Research Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University |
| Designed | 1950[1] |
| Manufacturer | Philco[1] Naval Ordnance Station Forest Park Leeds and Northrup |
| No. built | 3300[1] |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 700 pounds[1] |
| Length | 83 inches[1] |
| Diameter | 19 inches with 25.4-inch fins[1] |
| Effective firing range | 9600 yards[1] (24-minute search duration) |
| Warhead | Mk 32 Mod 1, HBX[1] |
| Warhead weight | 107 pounds[1] |
Detonation mechanism | Mk 19 Mods 4 and 11 contact exploder[1] |
| Engine | Electric[1] |
| Maximum speed | 12 knots[1] |
Guidance system | Helix search[1] |
Launch platform | Destroyers and aircraft[1] |
The Mark 32 torpedo was the first active acoustic antisubmarine homing torpedo in United States Navy service.[1] The Mark 32 was withdrawn from service use with the introduction of the Mark 43 torpedo.
Ten were manufactured by Leeds & Northrup, Philadelphia during War II, and about 3,300 were manufactured by a combination of the Philco Corporation, Philadelphia, and the Naval Ordnance Plant, Forest Park, Illinois.[1]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.