 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MK-7655 |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
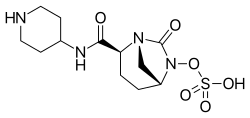
| Formula | C12H20N4O6S |
| Molar mass | 348.37 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Relebactam is a chemical compound used in combination with antibiotics to improve their efficacy. As a beta-lactamase inhibitor,[1] it blocks the ability of bacteria to break down a beta-lactam antibiotic. In the United States, relebactam is approved for use in the combination imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam (Recarbrio).[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Papp-Wallace KM, Barnes MD, Alsop J, Taracila MA, Bethel CR, Becka SA, et al. (June 2018). "Relebactam Is a Potent Inhibitor of the KPC-2 β-Lactamase and Restores Imipenem Susceptibility in KPC-Producing Enterobacteriaceae". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 62 (6). doi:10.1128/AAC.00174-18. PMC 5971601. PMID 29610205.
- ↑ "FDA approves new treatment for complicated urinary tract and complicated intra-abdominal infections". Food and Drug Administration. July 17, 2019.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.