 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
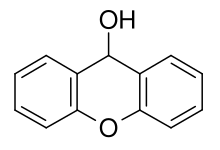
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Xanthen-9-ol | |
| Other names
Xanthanol, 9-Hydroxyxanthene, 9-Xanthydrol, Xanthen-9-ol, 9-Xanthenol, Xanthydrol solution | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 10395 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.815 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 198.221 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 124 to 126 °C (255 to 259 °F; 397 to 399 K)[1] |
| Hazards[2] | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H315, H319, H335, H411 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Xanthydrol is an organic chemical compound. Its formula is C13H10O2. Its total molecular weight is 198.221 g/mol. Xanthydrol is used to test the levels of urea in the bloodstream.[3]
Synthesis
See also
References
- ↑ Goldberg; Wragg (1957). "972. Spasmolytics derived from xanthen". Journal of the Chemical Society: 4823–4829. doi:10.1039/JR9570004823.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "9H-Xanthen-9-ol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ Bowden, R. S. T. (1962). "The Estimation of Blood Urea by the Xanthydrol Reaction". Journal of Small Animal Practice. 3 (4): 217–218. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.1962.tb04191.x.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.